WHAT IS SOIL RECLAMATION?
Every soil has a specific fertility level. If its level is very low, it can be improved through agrotechnical and agrochemical treatments. In nature, some soils have natural fertility. This is a characteristic of virgin soils, shaped by the influence of the natural environment. There are also soils with acquired fertility due to human activities.
MECHANICAL SOIL RECLAMATION
Soil quality can be improved through mechanical reclamation. Most often, agrotechnical treatments such as deep loosening and deep plowing are carried out.
Deep loosening involves loosening the deeper soil layers that have been excessively compacted. This procedure reaches much deeper than traditional cultivation tools. It is done using subsoilers, which loosen the soil to a depth of 40 to 80 cm. It is performed once every few years.
Deep plowing involves turning over the soil using a disc or moldboard plow and breaking it up. It is usually done to a depth of about 20–30 cm and is carried out as pre-winter plowing. It allows the soil to be left in the form of a „sharp slice.” This enables the soil to freeze and accumulate an adequate amount of water from thaws.
SOIL LIMING – IS IT WORTHWHILE?
Biological properties are as important as mechanical soil loosening treatments, ensuring good plant growth. It is very important to conduct laboratory soil tests. They will accurately determine the soil’s nutrient deficiencies and its pH level. With this information, effective agrochemical measures can be taken to reclaim the soil to the highest level possible.
If the soil pH is too low, it will be necessary to raise it through liming. The lime dosage is adjusted according to the soil type, the desired pH, and the type of plants to be planted in the area.
Low pH and acidic soil promote the development of fungal diseases and reduce plant resistance. Additionally, calcium deficiency combined with low pH blocks the seedlings’ ability to absorb other nutrients and nutrients from the soil. As a result, plant growth is limited, diseases are numerous, and yields are poor. Adequate soil pH and calcium content unlock the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients and micronutrients from the soil.
Soil liming not only raises the pH level and neutralizes the soil. Calcium ions are also necessary for proper plant growth. With this element, the plant can build its chromosomes and new cells. Calcium also affects enzyme activity and organic acid neutralization processes. Calcium deficiency for the plant also means a reduction in its ability to absorb water.

When to carry out liming?
Soil liming can be done in spring or autumn. As for the first of these terms, the field should be limed in early spring, at least a month before sowing or planting. It is also necessary to allow time between lime application and the application of other fertilizers in the field.
It is forbidden to combine soil liming with the application of potassium, sulfate, phosphate, and nitrogen fertilizers. Lime fertilizers contribute to significant nitrogen losses and reduce phosphorus uptake. Therefore, freshly manured soil should also not be limed. There must be a minimum interval of 2–3 weeks between the application of the above fertilizers and soil liming.
Liming can also be done in autumn, after harvesting in the field. The lime will then have more time to neutralize the soil. It is best to carry out this procedure on a warm, windless day. This will reduce lime losses associated with dusting. The soil should also not be too wet before liming.
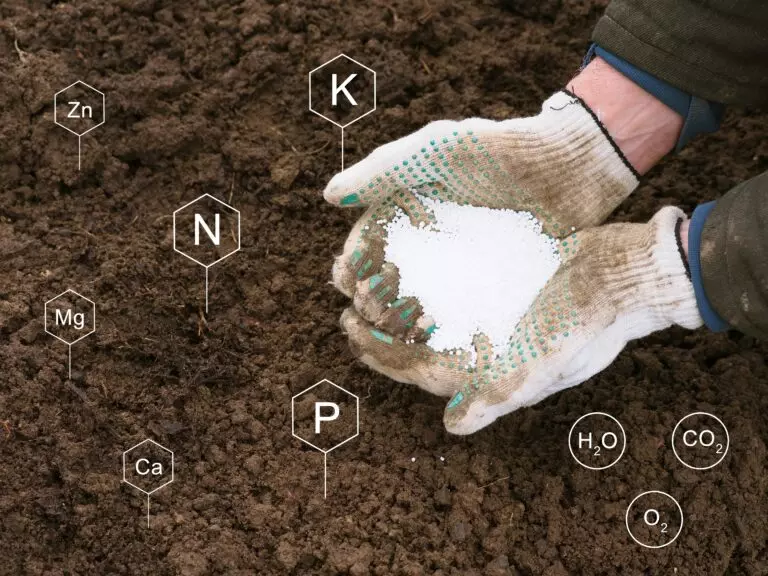

Which lime to choose for field liming?
The choice of lime for field liming depends primarily on the type of soil and its deficiencies in mineral nutrients. Depending on the soil type, different types of lime can be chosen:
- for liming medium and light soils, lime that acts slowly, such as carbonate and chalk lime, is suitable;
- for liming heavy soils, carbonate, chalk, and oxide lime can be used;
- for liming soils deficient in magnesium, preparations such as carbonate-magnesium or oxide-magnesium lime are suitable;
- for liming soils deficient in sulfur, calcium-sulfate fertilizers can be used, which stabilize the soil pH and enrich it with necessary minerals.
- An interesting form of liming is also granulated lime liming – oxide or carbonate form. It is more economical to use, reduces losses associated with its dusting during application, and mixes better with the soil. This effectively neutralizes the soil.